Progression & Assessment
Progression and Assessment (Key Stage 3): Progression simply means ‘getting better’. History teachers need models of what progression in history looks like but many contrasting models exist and lively debates continue. All history teachers therefore need to know enough to understand those debates and join them. History teachers and history education researchers have traditions of defining and testing goals for students, debating how far these should relate to substantive knowledge and/or disciplinary thinking, researching typical routes pupils take towards them and working out optimal paths to help them get there more securely. Read more
Sort by:
Date (Newest first) | Title A-Z
Show:
All |
Articles |
Podcasts |
Multipage Articles
-

'Assessing Pupil Progress'
ArticleClick to view -

A scaffold, not a cage: progression and progression models in history
ArticleClick to view -

Adventures in assessment
ArticleClick to view -

Assessment Without Levels
ArticleClick to view -

Assessment after levels
ArticleClick to view -

Assessment and planning for progression at Key Stage 3
ArticleClick to view -

Assessment of students' uses of evidence
ArticleClick to view -

Assessment without Level Descriptions
ArticleClick to view -

Building and assessing learner autonomy within the Key Stage 3 history classroom
ArticleClick to view -

Building meaningful models of progression
ArticleClick to view -
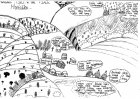
Creating a progression model for teaching historical perspectives in Key Stage 3
ArticleClick to view -

Creating controversy in the classroom: making progress with historical significance
ArticleClick to view -

Cunning Plan 162: Transferring knowledge from Key Stage 3 to 4
ArticleClick to view -

Cunning Plan 167: teaching the industrial revolution
ArticleClick to view -

Designing end-of-year exams: trials and tribulations
ArticleClick to view -

Developing independent learning with Year 7
ArticleClick to view -

Do's and Dont's in developing assessment practice
ArticleClick to view -

Effective essay introductions
ArticleClick to view -

Ensuring progression continues into GCSE: let's not do for our pupils with our plan of attack
ArticleClick to view -
Here ends the lesson: shaping lesson conclusions
ArticleClick to view

